一、第一个Mybatis项目
采用接口式编程
1. 创建maven工程并导包
可以使用maven在线下载依赖,这里因为我已经下载好了jar包,直接导入就行了
新建一个lib文件夹,导入 mysql 驱动 和 mybatis-3.4.1 并将lib文件夹右键 add as library
可在官网下载 mybatis 的 jar 包 mybatis 官网
2. 创建数据库表和对应的 JavaBean
数据库表
CREATE TABLE `tbl_employee` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`last_name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`gender` char(1) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;对应的 JavaBean
public class Employee {
Integer id;
String lastName; //字段名最好和数据库中的字段一致,如果不一致,可在sql语句中起别名
String gender;
String email;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String isGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id=" + id +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", gender=" + gender +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
'}';
}
}此处的 lastName 设置了和数据库中的字段 last_Name 是不一致的,我们在后面的配置文件中需要给数据库字段起对应的别名,否则会出错。
3. 创建Mybatis全局配置文件
MyBatis 的全局配置文件包含了影响 MyBatis 行为甚深 的设置(settings)和属性(properties)信息、如数据 库连接池信息等。指导着MyBatis进行工作。我们可以 参照官方文件的配置示例
新建 conf 文件夹,并右键 make Directory as source root
建立 mybatis-config.xml 全局配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--将我们写好的sql映射文件注册到全局配置文件中-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="EmployeeMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>mappers 中注册的 sql 映射文件如下
4. 创建一个Dao层接口
在该接口中定义要执行的方法
public interface EmployeeMapper {
public Employee getEmpById(Integer id);
}5. 创建sql映射文件 Mapper
映射文件的作用就相当于是定义数据库如何工作,编写sql语句。这也是我们使用MyBatis时编写的最多的文件。
同样在 conf 文件夹下,创建 EmployeeMapper.xml 用来编写 sql 语句
我们采用接口式编程,将接口中的方法和该映射文件绑定起来
- 修改名称空间 namespace 为接口的全类名
- 修改 id 为接口的方法名
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--名称空间,指定为接口的全类名-->
<mapper namespace="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper">
<!--id:唯一标识
resultType: 返回值类型
#{id}:从传递过来的参数中取出id值-->
<!--public Employee getEmpById(Integer id)
将唯一标识id和接口中的方法进行绑定-->
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select id, last_name lastName, email, gender from tbl_employee where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>6. 测试
首先,我们加载主配置文件,生成一个 SqlSessionFactory,再由 SqlSessionFactory 生成一个 SqlSession,一个 SqlSession 就相当于我们的一个会话,类似于 JDBC 中的 一个连接 connection,在 SQL 语句执行完毕后,这个会话是可以被关闭的。
SqlSession 的实例不是线程安全的,因此是不能被共享的。
SqlSession 每次使用完成后需要正确关闭,这个 关闭操作是必须的。通常把这个关闭操作放到 finally 块中
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException{
// 1. 获取sqlSessionFactory对象
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 2. 获取sqlSession实例
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
// 3. 获取接口的实现类对象
// Mybatis会为接口自动的创建一个代理对象,由代理对象去执行增删改查方法
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
// 4. 调用接口方法
Employee employee = mapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(employee);
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}二、全局配置文件
MyBatis 的配置文件包含了影响 MyBatis 行为甚深的 设置(settings)和属性(properties)信息。文档的顶层结构如下:
- configuration 配置
- properties 属性
- settings 设置
- typeAliases 类型命名
- typeHandlers 类型处理器
- objectFactory 对象工厂
- plugins 插件
- environments 环境
- environment 环境变量
- transactionManager 事务管理器
- dataSource 数据源
- databaseIdProvider 数据库厂商标识
- mappers 映射器
1. properties属性
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>相比于上述在全局配置文件中写死的方式,我们可以利用 peoperties 将数据库配置信息提取出来
mybatis 可以使用 properties 来引入外部 properties 配置文件的内容;
resource:引入类路径下的资源url:引入网络路径或者磁盘路径下的资源
<properties resource="dbconfig.properties"></properties>在 conf 文件夹下建立 dbconfig.properties 文件,将数据库配置信息写在此处
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root如果属性在不只一个地方进行了配置,那么 MyBatis 将按照下面的顺序来加载:
- 在 properties 元素体内指定的属性首先被读取。
- 然后根据 properties 元素中的 resource 属性读取类路径下属性文件或根 据 url 属性指定的路径读取属性文件,并覆盖已读取的同名属性。
- 最后读取作为方法参数传递的属性,并覆盖已读取的同名属性
2. settings 设置
这是 MyBatis 中极为重要的调整设置,它们会改变 MyBatis 的运行时行为
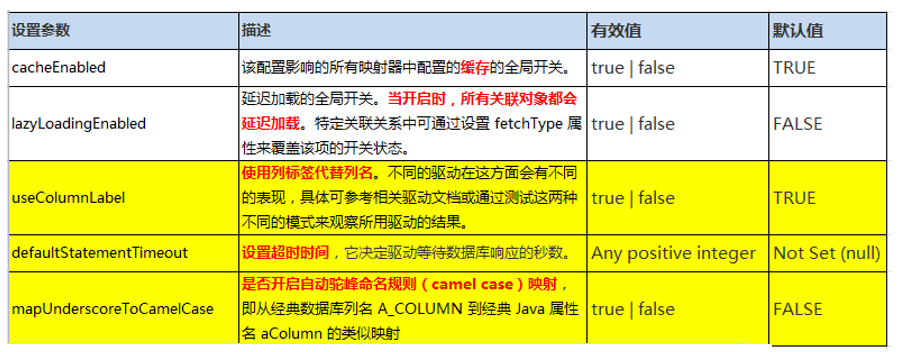
在之后用到这些标签的时候再详细讲解,此处我们先看 mapUnderscoreToCamelCase 参数.
把该参数设置为true,则打开驼峰命名法,像我们在第一节中数据库字段last_Name,JavaBean字段 lastName ,开启了该参数后,就不需要定义别名了,Myabtis 可以实现该字段的映射
<!-- settings包含很多重要的设置项
setting:用来设置每一个设置项
name:设置项名
value:设置项取值
-->
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>3. typeAliases 别名处理器
类型别名是为 Java 类型设置一个短的名字,可以方便我们 引用某个类, 别名不区分大小写
typeAlias: 为某个java类型起别名type: 指定要起别名的类型全类名;
alias: 指定新的别名。默认别名就是类名小写;
<typeAliases> <typeAlias type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" alias="emp"/> </typeAliases>类很多的情况下,可以批量设置别名,为这个包下的每一个类创建一个默认的别名,就是简单类名小写
<typeAliases> <!-- package:为某个包下的所有类批量起别名 name:指定包名(为当前包以及下面所有的后代包的每一个类都起一个默认别名(类名小写))--> <package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean"/> </typeAliases>批量起别名的情况下,使用
@Alias注解为某个类型指定新的别名@Alias("emp") public calss Employee{
值得注意的是,MyBatis已经为许多常见的 Java 类型内建 了相应的类型别名。它们都是大小写不敏感的,我们在 别名的时候千万不要占用已有的别名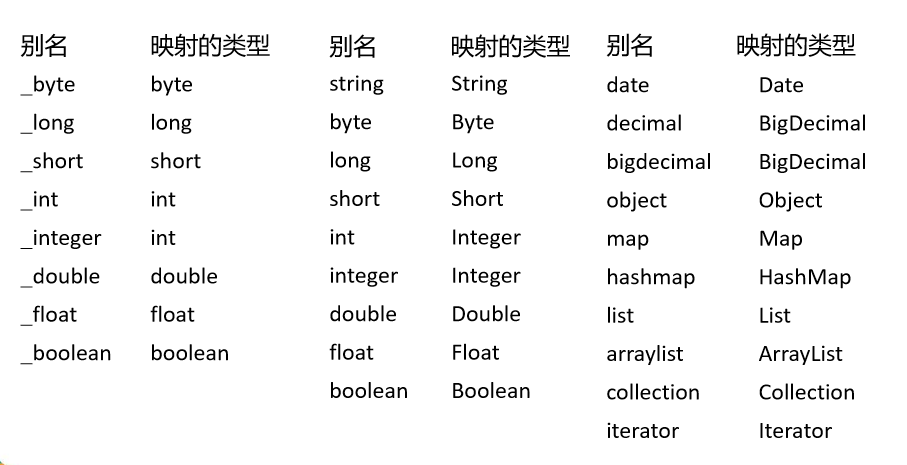
并不推荐用别名,使用全类名可以方便的 ctrl+左键 进入该类,不用到处找别名。
4. typeHandlers 类型处理器
无论是 MyBatis 在预处理语句(PreparedStatement)中 设置一个参数时,还是从结果集中取出一个值时, 都会用类型处理器将获取的值以合适的方式转换成 Java 类型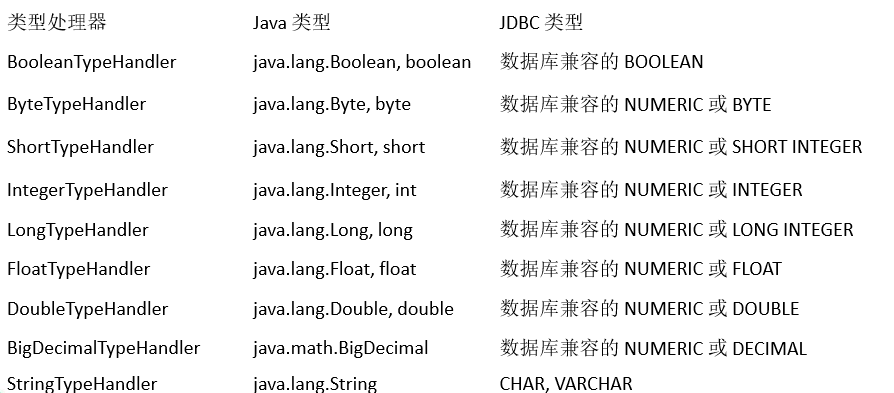
① 日期类型的处理
日期和时间的处理,JDK1.8以前一直是个头疼的 问题。我们通常使用JSR310规范领导者Stephen Colebourne创建的Joda-Time来操作。1.8已经实 现全部的JSR310规范了。
日期时间处理上,我们可以使用MyBatis基于 JSR310(Date and Time API)编写的各种日期 时间类型处理器。
MyBatis3.4以前的版本需要我们手动注册这些处 理器,以后的版本都是自动注册
② 自定义类型处理器
我们可以重写类型处理器或创建自己的类型处理 器来处理不支持的或非标准的类型。
步骤:
1)
实现org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandler接口或 者继承org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler2)指定其映射某个JDBC类型(可选操作)
3)在mybatis全局配置文件中注册
5. plugins 插件
插件是MyBatis提供的一个非常强大的机制,我们 可以通过插件来修改MyBatis的一些核心行为。插件通过动态代理机制,可以介入四大对象的任何一个方法的执行。后面会有专门的章节来介绍 mybatis 运行原理以及插件
先来熟悉以下四大对象
- 执行器:
Executor(update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed) - 参数处理器:
ParameterHandler(getParameterObject, setParameters) - 结果集处理器:
ResultSetHandler(handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters) - sql 语句处理器:
StatementHandler(prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
6. environments 环境
MyBatis可以配置多种环境,比如开发、测试和生产环境需要有不同的配置。
每种环境使用一个
environment标签进行配置并指定唯一标识符可以通过 environments 标签中的
default属性指定 一个环境的标识符来快速的切换环境<environments default="dev_mysql"> <environment id="dev_mysql"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> <environment id="dev_oracle"> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${orcl.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${orcl.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${orcl.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${orcl.password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>id:指定当前环境的唯一标识transactionManager和dataSource都必须有
① transactionManager
type: JDBC | MANAGED | 自定义
JDBC:使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,依赖于从数 据源得到的连接来管理事务范围。 JdbcTransactionFactory
MANAGED:不提交或回滚一个连接、让容器来管理 事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下 文)。 ManagedTransactionFactory
自定义:实现TransactionFactory接口,type=全类名/ 别名
② dataSource
type: UNPOOLED | POOLED | JNDI | 自定义
- UNPOOLED:不使用连接池, UnpooledDataSourceFactory
- POOLED:使用连接池, PooledDataSourceFactory
- JNDI: 在EJB 或应用服务器这类容器中查找指定的数据源
- 自定义:实现DataSourceFactory接口,定义数据源的 获取方式。
实际开发中我们使用Spring管理数据源,并进行事务控制的配置来覆盖上述配置
7. databaseIdProvider 环境
MyBatis 可以根据不同的数据库厂商执行不同的语句。
databaseIdProvider:支持多数据库厂商的;
type="DB_VENDOR" :VendorDatabaseIdProvider 作用就是得到数据库厂商的标识 (驱动getDatabaseProductName()),mybatis就能根据数据库厂商标识来执行不同的sql;
- MySQL
- Oracle
- SQL Server
- 。。。。。。
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR">
<!-- 为不同的数据库厂商起别名 -->
<property name="MySQL" value="mysql"/>
<property name="Oracle" value="oracle"/>
<property name="SQL Server" value="sqlserver"/>
</databaseIdProvider><select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"
databaseId="mysql">
select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"
databaseId="oracle">
select EMPLOYEE_ID id,LAST_NAME lastName,EMAIL email
from employees where EMPLOYEE_ID=#{id}
</select>MyBatis 匹配规则如下:
如果没有配置 databaseIdProvider 标签,那么 databaseId=null
如果配置了databaseIdProvider 标签,使用标签配置的 name 去匹配数据库信息,匹配上设置databaseId = 配置指定的值,否则依旧为 null
如果 databaseId 不为null,他只会找到配置databaseId的sql语句
MyBatis 会加载不带 databaseId 属性和带有匹配当前数据库 databaseId 属性的所有语句。如果同时找到带有 databaseId 和不带 databaseId 的相同语句,则后者会被舍弃。
8. mapper 映射
mapper逐个注册SQL映射文件
<!-- mappers:将sql映射注册到全局配置中 --> <mappers> <!-- mapper:注册一个sql映射 注册配置文件 resource:引用类路径下的sql映射文件 mybatis/mapper/EmployeeMapper.xml url:引用网路路径或者磁盘路径下的sql映射文件 file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml --> <mapper resource="mybatis/mapper/EmployeeMapper.xml"/> </mappers>⭐ 也可以采用 注册接口 的方法
class:引用(注册)接口,有 sql 映射文件,映射文件名必须和接口同名,并且放在与接口同一目录下;
<mapper class="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperAnnotation"/>没有sql映射文件,所有的 sql 都是利用注解写在接口上;
@Select("select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id}") public Employee getEmeById(Integer id){}推荐:
- 比较重要的,复杂的 Dao 接口我们来写 sql 映射文件
- 不重要,简单的 Dao 接口为了开发快速可以使用注解;
批量注册
这种方式要求SQL映射文件名必须和接口名相同并且在同一目录下
<mappers> <!-- 批量注册: --> <package name="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao"/> <mappers>
三、sql映射文件
映射文件指导着MyBatis如何进行数据库增删改查, 有着非常重要的意义;
- cache –命名空间的二级缓存配置
- cache-ref – 其他命名空间缓存配置的引用
- resultMap – 自定义结果集映射
- parameterMap – 已废弃!老式风格的参数映射
- sql –抽取可重用语句块。
- insert – 映射插入语句
- update – 映射更新语句
- delete – 映射删除语句
- select – 映射查询语句
1. 增删改查 insert、update、delete、select
查 select 元素在上面章节已经学习过了,接下来看 insert, update, delete 元素,在第一节代码的基础上完成一套完整的 CRUD 流程
mybatis 允许增删改直接定义以下类型返回值
- Integer
- Long
- Boolean
- void
Dao层接口类:
public interface EmployeeMapper {
/**
* 查找
* @param id
* @return
*/
public Employee getEmpById(Integer id);
/**
* 更新
* @param employee
* @return
*/
public boolean updateEmp(Employee employee);
/**
* 添加
* @param employee
* @return
*/
public Integer addEmp(Employee employee);
/**
* 删除
* @param id
*/
public void deleteEmpById(Integer id);
}sql 映射文件:
<mapper namespace="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper">
<!--id:唯一标识
resultType: 返回值类型
#{id}:从传递过来的参数中取出id值-->
<!--public Employee getEmpById(Integer id)
将唯一标识id和接口中的方法进行绑定-->
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select id, last_name lastName, email, gender from tbl_employee where id = #{id}
</select>
<!--public Integer addEmp(Employee employee);-->
<insert id = "addEmp">
insert into tbl_employee(last_name, email, gender) values(#{lastName}, #{email}, #{gender})
</insert>
<!--public boolean updateEmp(Employee employee);-->
<update id="updateEmp" >
update tbl_employee
set last_name = #{lastName}, email = #{email}, gender = #{gender}
where id = #{id}
</update>
<!--public void deleteEmpById(Integer id);-->
<delete id="deleteEmpById">
delete from tbl_employee
where id = #{id}
</delete>
</mapper>同时别忘了在 JavaBean 类中添加无参构造函数和构造函数,以及在全局配置文件中注册 sql 映射文件
/**
* 测试增删改
* * 1、mybatis允许增删改直接定义以下类型返回值
* * Integer、Long、Boolean、void
* * 2、我们需要手动提交数据
* * sqlSessionFactory.openSession();===》手动提交
* * sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);===》自动提交
*/
@Test
public void test02() throws IOException{
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
// 测试插入
Employee jack = new Employee(null, "Jack", "1", "Jack@qq.com");
mapper.addEmp(jack);
// 测试修改
Employee jack123 = new Employee(2, "Jack123", "0", "Jack123@qq.com");
mapper.updateEmp(jack123);
// 测试删除
mapper.deleteEmpById(2);
//必须手动提交数据
sqlSession.commit();
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}注意一定要手动提交数据 sqlSession.commit();
因为我们是这样打开的 sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
可以通过 sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); 来设置自动提交
2. insert 获取自增主键的值
若数据库支持自动生成主键的字段(比如 MySQL 和 SQL Server),
则可以设置 useGeneratedKeys=”true”,然后再把 keyProperty 设置到目标属性上。
<insert id="addEmp" parameterType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee"
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender)
values(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender})
</insert>3. 参数处理
① 单个参数
单个参数:mybatis不会做特殊处理,#{参数名/任意名}:取出参数值
例如:
public Employee getEmpById(Integer id);不一定非要通过 #{id} 取出参数值,任意参数名都可取出,比如 #{abc}
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where id = #{abc}
</select>② 多个参数
多个参数的情况下,按照上面的方法取值会报错,比如:
public Employee getEmpByIdAndLastName(Integer id,String lastName);
-------------------------------------------------------------------
<select id="getEmpByIdAndLastName" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id} and last_name=#{lastName}
</select>报错如下:
org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException:
Parameter 'id' not found.
Available parameters are [1, 0, param1, param2]任意多个参数,都会被 MyBatis 重新包装成一个Map传入。
key:param1…paramN, 或者参数的索引也可以
value:传入的参数值
#{ } 就是从 map 中获取指定的 key 的值
<select id="getEmpByIdAndLastName" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where id = #{param1} and last_name= #{param2}
</select>③ @Param 命名参数
多个参数用上述这样的方法看起来不太直观,于是我们可以使用注解 @Param 为参数起一个名字,MyBatis就会将这些参数封装进 map 中,key 就是我们自己指定的名字
举例如下:
public Employee getEmpByIdAndLastName(@Param("id")Integer id,@Param("lastName")String lastName);
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<select id="getEmpByIdAndLastName" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id} and last_name = #{lastName}
</select>④ POJO
如果多个参数正好是我们业务逻辑的数据模型,我们就可以直接传入pojo;
#{属性名}:取出传入的pojo的属性值
举例如下:
public boolean updateEmp(Employee employee);
-------------------------------------------------------------
<update id="updateEmp">
update tbl_employee
set last_name=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender}
where id=#{id}
</update>⑤ Map
如果多个参数不是业务模型中的数据,没有对应的pojo,不经常使用,为了方便,我们也可以封装多个参数为 map,直接传递
#{key}:取出map中对应的值
举例如下:
public Employee getEmpByMap(Map<String, Object> map);
---------------------------------------------------------------------
<select id="getEmpByMap" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where id=${id} and last_name=#{lastName}
</select>EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
//Employee employee = mapper.getEmpByIdAndLastName(1, "tom");
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", 2);
map.put("lastName", "Tom");
Employee employee = mapper.getEmpByMap(map);⑥ TO
如果多个参数不是业务模型中的数据,但是经常要使用,推荐来编写一个 TO(Transfer Object) 数据传输对象
比如分页模型
Page{
int index;
int size;
......
}参数处理综合示例
public Employee getEmp(@Param("id")Integer id,String lastName);取值:
- id —>
#{id / param1} - lastName —>
#{param2}
public Employee getEmp(Integer id,@Param("e")Employee emp);取值:
- id —>
#{param1} - lastName —>
#{param2.lastName / e.lastName}
特别注意:
如果是Collection(List、Set)类型或者是数组,也会特殊处理。也是把传入的 list 或者数组封装在 map 中。
- Collection:则对应 key 为 collection
- List:则对应 key 为 collection 或者 list
举例如下:
public Employee getEmpById(List<Integer> ids);取出第一个id的值: #{list[0]}
参数处理 $ 和 # 的区别
#{}:可以获取 map 中的值或者 pojo 对象属性的值;${}:可以获取 map 中的值或者 pojo 对象属性的值;
select * from tbl_employee where id = ${id} and last_name= #{lastName}输出如下:
Preparing: select * from tbl_employee where id=2 and last_name=?
区别:
#{}: 是以预编译的形式,将参数设置到 sql 语句中,防止 sql 注入${}: 取出的值直接拼装在sql语句中;会有安全问题;
大多情况下,我们去参数的值都应该去使用 #{};
原生jdbc不支持占位符的地方我们就可以使用 ${} 进行取值
比如分表、排序。。。;
举例如下:
按照年份分表拆分
select * from ${year}_salary where xxx;
select * from tbl_employee order by ${f_name} ${order}3. select 元素
Select 元素来定义查询操作。
Id:唯一标识符。 — 用来引用这条语句,需要和接口的方法名一致parameterType:参数类型。 – 可以不传,MyBatis会根据TypeHandler自动推断resultType:返回值类型。 – 别名或者全类名,如果返回的是集合,定义集合中元 素的类型。不能和 resultMap 同时使用
① resultType 返回值类型
a. 返回对象
返回类型是对象的情况我们之前已经反复使用过了,下面来讲解以下其他返回类型
b. 返回 List
如果返回的是集合,resultType 中定义集合中的元素的类型,比如下面代码中的 Employee
public List<Employee> getEmpsByLastNameLike(String lastName);
--------------------------------------------------------------
<!--resultType:如果返回的是一个集合,要写集合中元素的类型 -->
<select id="getEmpsByLastNameLike" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where last_name like #{lastName}
</select>测试:
List<Employee> like = mapper.getEmpsByLastNameLike("%e%");
for (Employee employee : like) {
System.out.println(employee);
}c. 返回 Map
resultmap = "map"
返回一条记录
返回一条记录的 map;key就是列名,值就是对应的值
public Map<String, Object> getEmpByIdReturnMap(Integer id);
-------------------------------------------------------
<select id="getEmpByIdReturnMap" resultType="map">
select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id}
</select>测试:
Map<String, Object> map = mapper.getEmpByIdReturnMap(1);
System.out.println(map);结果:
{id = 1, email=jack@qq.com, last_name = Jack, gender = 0}
返回多条记录
- 多条记录封装一个map:
Map<Integer,Employee>: 键是这条记录的主键,值是记录封装后的javaBean @MapKey: 告诉mybatis封装这个 map 的时候使用哪个属性作为 map 的 key
@MapKey("lastName")
public Map<String, Employee> getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap(String lastName);
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
<select id="getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap"
resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where last_name like #{lastName}
</select>测试:
Map<String, Employee> map = mapper.getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap("%r%");
System.out.println(map);结果:
{Jack = Employee[id = 1, lastName = Jack, email = jack@qq.com, gender = 0],Tom = Employee[id = 2, lastName = Tom, email = tom@qq.com, gender = 1]}
② resultMap 自定义结果集映射规则
resultType 自定义某个 JavaBean 的封装规则
参数:
- type:自定义规则的 JavaBean 类型
- id: 唯一id方便引用
标签:
- id : 定义主键
- result:定义其他普通键
标签属性:
- column : 数据库表的列名
- property : 对应的JavaBean属性
<resultMap type="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MySimpleEmp">
<!--指定主键列的封装规则
id 定义主键 底层会有优化;
column:指定哪一列
property:指定对应的javaBean属性
result 定义普通列封装规则
-->
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<!-- 其他不指定的列会自动封装:但是 推荐 我们只要写resultMap就把全部的映射规则都写上-->
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- resultMap:自定义结果集映射规则; -->
<!-- public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); -->
<select id="getEmpById" resultMap="MySimpleEmp">
select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id}
</select>③ resultMap 联合查询:级联属性封装结果集
- POJO 中的属性可能会是一个对象
- 我们可以使用联合查询,并以级联属性的方式封装对象。
例如:员工表中含有部门对象
实体类:
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private String gender;
private Department dept;
--------------------------------------------------
public class Department {
private Integer id; //数据库表字段id
private String departmentName; //数据库表字段dept_name接口:
public Employee getEmpAndDept(Integer id);映射文件:
employee 中内嵌对象 dept 的属性通过 dept.id、dept.departmentName 等来获取
<!--
联合查询:级联属性封装结果集
-->
<resultMap type="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyDifEmp">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<result column="did" property="dept.id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="dept.departmentName"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Employee getEmpAndDept(Integer id);-->
<select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="MyDifEmp">
SELECT e.id id,e.last_name last_name,e.gender gender,e.d_id d_id,
d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name FROM tbl_employee e,tbl_dept d
WHERE e.d_id=d.id AND e.id=#{id}
</select>④ resultMap association:嵌套结果集
使用association定义关联的单个对象的封装规则
association 标签可以指定联合的 javaBean 对象
property= “dept” :指定哪个属性是联合的对象javaType: 指定这个属性对象的类型[不能省略]
<!--
使用association定义关联的单个对象的封装规则;
-->
<resultMap type="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyDifEmp2">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<!-- association可以指定联合的javaBean对象
property="dept":指定哪个属性是联合的对象
javaType:指定这个属性对象的类型[不能省略]
-->
<association property="dept" javaType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Department">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Employee getEmpAndDept(Integer id);-->
<select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="MyDifEmp2">
SELECT e.id id,e.last_name last_name,e.gender gender,e.d_id d_id,
d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name FROM tbl_employee e,tbl_dept d
WHERE e.d_id=d.id AND e.id=#{id}
</select>⑤ resultMap association:分步查询
使用 association 进行分步查询:
先按照员工 id 查询员工信息
select * from tbl_employee where id = 1;根据查询到的员工信息中的 d_id 值去部门表查出部门信息
select * from tbl_dept where id = 1;将部门信息设置到员工中;
association 标签的相关属性
select: 表明当前属性是调用 select 指定的方法查出的结果column: 指定将哪一列的值传给这个方法
流程 :使用 select 指定的方法(传入column 指定的这列参数的值)查出对象,并封装给 property 指定的属性
<!-- id last_name email gender d_id -->
<resultMap type="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyEmpByStep">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<!-- association定义关联对象的封装规则
select:表明当前属性是调用select指定的方法查出的结果
column:指定将哪一列的值传给这个方法
流程:使用select指定的方法(传入column指定的这列参数的值)查出对象,并封装给property指定的属性
-->
<association property="dept"
select="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper.getDeptById"
column="d_id">
</association>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Employee getEmpByIdStep(Integer id);-->
<select id="getEmpByIdStep" resultMap="MyEmpByStep">
select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id}
</select>
其中,根据部门 id 查询部门信息 getDeptById 如下:
public Department getDeptByIdStep(Integer id);
-------------------------------------------
<select id="getDeptById" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Department">
select id,dept_name departmentName from tbl_dept where id=#{id}
</select>⑥ resultMap association:分步查询 & 延迟加载
在分步查询基础上实现延迟加载(懒加载)
在全局配置文件中开启延迟加载和属性按需加载
<settings>
<!--显示的指定每个我们需要更改的配置的值,即使他是默认的。防止版本更新带来的问题 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings>⑦ resultMap collection:嵌套结果集
场景:查询部门的时候将部门对应的所有员工信息也查询出来
部门表对应的JavaBean,内嵌员工信息的集合属性
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String departmentName;
private List<Employee> emps;public List<Employee> getEmpsByDeptId(Integer deptId);
--------------------------------------------
<select id="getEmpsByDeptId" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where d_id= #{deptId}
</select>collection 标签定义关联集合类型的属性的封装规则
参数:
property:指定要封装到哪个集合属性(本例中封装到部门对象中的 emps 属性)ofType: 指定集合里面元素的类型
<!--嵌套结果集的方式,使用collection标签定义关联的集合类型的属性封装规则 -->
<resultMap type="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Department" id="MyDept">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/>
<!--
collection定义关联集合类型的属性的封装规则
ofType:指定集合里面元素的类型
-->
<collection property="emps" ofType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
<!-- 定义这个集合中元素的封装规则 -->
<id column="eid" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Department getDeptByIdPlus(Integer id); -->
<select id="getDeptByIdPlus" resultMap="MyDept">
SELECT d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name,
e.id eid,e.last_name last_name,e.email email,e.gender gender
FROM tbl_dept d
LEFT JOIN tbl_employee e
ON d.id=e.d_id
WHERE d.id=#{id}
</select>
⑧ resultMap collection:分步查询
需求:根据部门 id 查询该部门下所有的员工信息
- 根据部门 id 查询部门信息
- 根据部门 id 查询员工信息
<!-- collection:分段查询 -->
<resultMap type="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Department" id="MyDeptStep">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<id column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/>
<collection property="emps"
select="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperPlus.getEmpsByDeptId"
column="id">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Department getDeptByIdStep(Integer id); -->
<select id="getDeptByIdStep" resultMap="MyDeptStep">
select id,dept_name from tbl_dept where id=#{id}
</select>其中根据部门id查询员工信息 getEmpsByDeptId
public List<Employee> getEmpsByDeptId(Integer deptId);
-------------------------------------------
<select id="getEmpsByDeptId" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where d_id=#{deptId}
</select>⑨ resultMap collection:多列值封装map & 懒加载
分步查询的时候通过column指定,将对应的列的数据传递过去,我们有时需要传递多列数据 :将多列的值封装 map 传递;
column="{key1=column1,key2=column2}"
key是方法中的形参,column是数据库表列名
fetchType="lazy" :表示使用延迟加载,该标签可以覆盖全局的延迟加载策略
- lazy:延迟
- eager:立即
<resultMap type="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Department" id="MyDeptStep">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<id column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/>
<collection property="emps"
select="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperPlus.getEmpsByDeptId"
column="{deptId=id}" fetchType="lazy"></collection>
</resultMap>⑩ resultMap discriminator 鉴别器
鉴别器:mybatis可以使用 discriminator 判断某列的值,然后根据某列的值改变封装行为
<discriminator javaType=" " column = " "></discriminator>
属性:
- column:指定判定的列名
- javaType:列值对应的java类型
场景:
- 如果查出的是女生:就把部门信息查询出来,否则不查询;
- 如果是男生,把 last_name 这一列的值赋值给 email;
<resultMap type="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyEmpDis">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<!--
column:指定判定的列名
javaType:列值对应的java类型 -->
<discriminator javaType="String" column="gender">
<!--女生 resultType:指定封装的结果类型;不能缺少-->
<case value="0" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
<association property="dept"
select="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper.getDeptById"
column="d_id">
</association>
</case>
<!--男生 ;如果是男生,把last_name这一列的值赋值给email; -->
<case value="1" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="last_name" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
</case>
</discriminator>
</resultMap>四、动态 SQL
动态 SQL是MyBatis强大特性之一。极大的简化我们拼装 SQL的操作。 动态 SQL 元素和使用 JSTL 或其他类似基于 XML 的文本处 理器相似。MyBatis 采用功能强大的基于 OGNL 的表达式来简化操作。
- if 判断
- choose (when, otherwise) 分支选择
- trim (where, set) 字符串截取
- foreach 遍历集合
1. if 判断 & OGNL 判断表达式
public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionIf(Employee employee);查询员工,要求:携带了哪个字段查询条件就带上这个字段的值
<!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionIf(Employee employee); -->
<select id="getEmpsByConditionIf" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where
<!-- test:判断表达式(OGNL)从参数中取值进行判断 -->
<if test="id!=null">
id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="lastName!=null and lastName!=''">
and last_name like #{lastName}
</if>
<if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=''">
and email=#{email}
</if>
<!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 -->
<if test="gender==0 or gender==1">
and gender=#{gender}
</if>
</select>如果查询字段email为空
Employee employee = new Employee(1, "Admin", null, 1);
List<Employee> emps = mapper.getEmpsByConditionIf(employee );则查询语句为
select * from tbl_employee where id = ? and last_name = ? and gender = ?2. where 查询条件
上述写法我们可以看见一个问题,如果 id = null,那么查询语句就变成
select * from tbl_employee where and last_name = ? and gender = ?语法出错,and 被强行拼接,解决方法有两种:
👍 在
selet * from table_name后面加上where 1 = 1,并在所有的条件语句都加上and前缀则如果 id = null,那么查询语句任然成立
<!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionIf(Employee employee); --> <select id="getEmpsByConditionIf" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee where 1 = 1 <if test="id!=null"> and id=#{id} </if> <if test="lastName!=null and lastName!=''"> and last_name like #{lastName} </if> <if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=''"> and email=#{email} </if> <!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 --> <if test="gender==0 or gender==1"> and gender=#{gender} </if> </select>select * from tbl_employee where 1 = 1 and last_name = ? and gender = ?将 if 判断语句全都写在
where标签中<select id="getEmpsByConditionIf" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee"> select * from tbl_employee <!-- where --> <where> <if test="id!=null"> and id=#{id} </if> <if test="lastName!=null and lastName!= ''"> and last_name like #{lastName} </if> <if test="email!=null and email.trim()!= ''"> and email=#{email} </if> <!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 --> <if test="gender==0 or gender==1"> and gender=#{gender} </if> </where> </select>where 会自动剔除多出来的 第一个前缀 and 或者 or
可以看见,上述的做法依然存在漏洞,如果我们的写法是把and放在后面:
<select id="getEmpsByConditionIf" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee
<where>
<if test="id!=null">
id=#{id} and
</if>
<if test="lastName!=null and lastName!= ''">
last_name like #{lastName} and
</if>
<if test="email!=null and email.trim()!= ''">
email=#{email} and
</if>
<!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 -->
<if test="gender==0 or gender==1">
gender=#{gender}
</if>
</where>
</select>如果 gender 为空,则查询语句为
select * from tbl_employee id = ? and last_name = ? and email = ? and语法出错,因为 where 只能剔除多出来的 第一个前缀 and 或者 or
所以,在使用 where 标签的时候,建议把 and 写在语句的前面
3. trim 自定义字符串截取
对于上述把 and 写在后面的写法,我们可以使用 trim 标签 自定义字符串的截取规则
trim 标签中的属性:
prefix=""前缀:trim标签体中是整个字符串拼串后的结果 prefix 给拼串后的整个字符串加一个前缀prefixOverrides=""前缀覆盖: 去掉整个字符串前面多余的字符suffix=""后缀:suffix给拼串后的整个字符串加一个后缀suffixOverrides=""后缀覆盖:去掉整个字符串后面多余的字符
<select id="getEmpsByConditionTrim" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee
<trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and">
<if test="id!=null">
id=#{id} and
</if>
<if test="lastName!=null && lastName!=""">
last_name like #{lastName} and
</if>
<if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=""">
email=#{email} and
</if>
<!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 -->
<if test="gender==0 or gender==1">
gender=#{gender}
</if>
</trim>
</select>4. choose 分支选择
choose (when, otherwise): 分支选择;
等同于 带了 break 的 swtich-case
如果带了 id 就用 id 查,如果带了 lastName 就用 lastName 查 ; 只会进入其中一个查询语句
<select id="getEmpsByConditionChoose" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee
<where>
<!-- 如果带了id就用id查,如果带了lastName就用lastName查;只会进入其中一个 -->
<choose>
<when test="id!=null">
id=#{id}
</when>
<when test="lastName!=null">
last_name like #{lastName} // 模糊查询
</when>
<when test="email!=null">
email = #{email}
</when>
<otherwise>
gender = 0 //如果上述条件都不符合,则执行此条语句
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>如果 id != null
Employee employee = new Employee(1, "Admin", null, null);
List<Employee> emps = mapper.getEmpsByConditionIf(employee );则查询语句为
select * from tbl_employee id = 1如果 全为 null
Employee employee = new Employee(null, null, null, null);
List<Employee> emps = mapper.getEmpsByConditionIf(employee );则查询语句为
select * from tbl_employee gender = 0 5. set 更新
我们之前的更新操作语句是这样的
<update id="updateEmp">
update tbl_employee
set last_name=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender}
where id=#{id}
</update>需要进行全字段更新
比如:已有数据库信息 id = 1 , lastName = Jack, email = 123, gender = 1;
我们想要更新它的lastName,则:
Employee employee = new Employee(1, "Admin", 123, 1);
List<Employee> emps = mapper.updateEmp(employee );set 标签用来执行更新操作,只更新需要更新的字段:
<!--public void updateEmp(Employee employee); -->
<update id="updateEmp">
<!-- Set标签的使用 -->
update tbl_employee
<set>
<if test="lastName!=null">
last_name=#{lastName},
</if>
<if test="email!=null">
email=#{email},
</if>
<if test="gender!=null">
gender=#{gender}
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>set 标签会自动剔除多余的 ,
比如:已有数据库信息 id = 1 , lastName = Jack, email = 123, gender = 1;
我们想要更新它的 lastName,则:
Employee employee = new Employee(1, "Admin", null, null);
List<Employee> emps = mapper.updateEmp(employee );可以看见 email 和 gender 都为空,即该字段不被更新,保持不变。
6. foreach 遍历集合
foreach 标签中的属性:
collection:指定要遍历的集合:
list类型的参数会特殊处理封装在map中,map的key就叫list
item:将当前遍历出的元素赋值给指定的变量
separator :每个元素之间的分隔符
open :遍历出所有结果拼接一个开始的字符
close : 遍历出所有结果拼接一个结束的字符
index : 索引。遍历list的时候是index就是索引,item就是当前值
遍历map的时候index表示的就是map的key,item就是map的值#{变量名}就能取出变量的值也就是当前遍历出的元素
① 批量查询
//查询员工id'在给定集合中的
public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionForeach(@Param("ids")List<Integer> ids);<!--public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionForeach(List<Integer> ids); -->
<select id="getEmpsByConditionForeach" resultType="com.smallbeef.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee
<foreach collection="ids" item="item_id" separator=","open="where id in(" close=")">
#{item_id}
</foreach>
</select>测试:
List<Employee> list = mapper.getEmpsByConditionForeach(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4));
for (Employee emp : list)
System.out.println(emp);② 批量保存
public void addEmps(@Param("emps")List<Employee> emps);<!--public void addEmps(@Param("emps")List<Employee> emps); -->
<!--MySQL下批量保存:可以foreach遍历 mysql支持values(),(),()语法-->
<insert id="addEmps">
insert into tbl_employee
values
<foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator=",">
(#{emp.lastName},#{emp.email},#{emp.gender},#{emp.dept.id})
</foreach>
</insert>测试:
@Test
public void testBatchSave() throws IOException{
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
EmployeeMapperDynamicSQL mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapperDynamicSQL.class);
List<Employee> emps = new ArrayList<>();
emps.add(new Employee(null, "smith0x1", "smith0x1@qq.com", "1",new Department(1)));
emps.add(new Employee(null, "allen0x1", "allen0x1@qq.com", "0",new Department(1)));
mapper.addEmps(emps);
openSession.commit();
}finally{
openSession.close();
}
}7. 两个内置参数 _databaseId / _parameter
两个内置参数:不只是方法传递过来的参数可以被用来判断,取值
mybatis默认还有两个内置参数:
_parameter: 代表整个参数单个参数:_parameter 就是这个参数
多个参数:参数会被封装为一个map;_parameter就是代表这个map
_databaseId: 如果配置了databaseIdProvider标签。_databaseId 就是代表当前数据库的别名 oracle
<!--public List<Employee> getEmpsTestInnerParameter(Employee employee); -->
<select id="getEmpsTestInnerParameter" resultType="com.smakk.mybatis.bean.Employee">
<if test="_databaseId=='mysql'">
select * from tbl_employee
<if test="_parameter!=null">
where last_name like #{lastName}
</if>
</if>
<if test="_databaseId=='oracle'">
select * from employees
<if test="_parameter!=null">
where last_name like #{_parameter.lastName}
</if>
</if>
</select>8. bind 绑定
bind 元素可以从 OGNL 表达式中创建一个变量并将其绑定到上下文。
比如:
<!--public List<Employee> getEmpsTestInnerParameter(Employee employee); -->
<select id="getEmpsTestInnerParameter" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
<bind name="_lastName" value="'%'+lastName+'%'"/>
<if test="_databaseId=='mysql'">
select * from tbl_employee
<if test="_parameter!=null">
where last_name like #{lastName}
</if>
</if>
</select>测试:
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setLastName("e");
List<Employee> list = mapper.getEmpsTestInnerParameter(employee2);
for (Employee employee : list)
System.out.println(employee);
lastName 的值 e 被 bind 拼接成 %e%,即由精确查询 —> 模糊查询
9. 抽取可重用的 sql 片段
抽取可重用的sql片段。方便后面引用
sql抽取:经常将要查询的列名,或者插入用的列名抽取出来方便引用include来引用已经抽取的sql:include 还可以自定义一些
property,可在sql标签内部通过${prop}取出对应值不能使用这种方式
#{prop}
示例如下:
<sql id="insertColumn">
<if test="_databaseId=='oracle'">
employee_id,last_name,email,${testColumn}
</if>
<if test="_databaseId=='mysql'">
last_name,email,gender,d_id
</if>
</sql><insert id="addEmps" databaseId="oracle">
insert into employees(
<!-- 引用外部定义的 sql -->
<include refid="insertColumn">
<property name="testColomn" value="abc"/>
</include>
)
<foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator="union"
open="select employees_seq.nextval,lastName,email from("
close=")">
select #{emp.lastName} lastName, #{emp.email} email from dual
</foreach>
</insert>五、缓存机制
MyBatis 包含一个非常强大的查询缓存特性,它可以非 常方便地配置和定制。缓存可以极大的提升查询效率。
MyBatis系统中默认定义了两级缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存。
- 默认情况下,只有一级缓存(SqlSession 级别的缓存, 也称为本地缓存)开启。
- 二级缓存需要手动开启和配置,他是基于 namespace 级别的缓存。(也称为全局缓存)
- 为了提高扩展性。MyBatis 定义了
缓存接口 Cache。我们 可以通过实现 Cache 接口来自定义二级缓存
1. 一级缓存(本地缓存)
一级缓存(本地缓存):sqlSession 级别的缓存。
- 一级缓存是一直开启的
- SqlSession 级别的一个 Map
- 与数据库同一次会话期间查询到的数据会放在本地缓存中。以后如果需要获取相同的数据,直接从缓存中拿,没必要再去查询数据库;
一级缓存失效情况(没有使用到当前一级缓存的情况,还需要再向数据库重新发出sql语句进行查询):
- sqlSession不同
- sqlSession相同,查询条件不同.(当前一级缓存中还没有这个数据)
- sqlSession相同,两次查询之间执行了增删改操作(因为这次增删改可能对当前数据有影响)
- sqlSession相同,手动清除了一级缓存(缓存清空)
openSession.clearCache();
2. 二级缓存(全局缓存)
二级缓存(全局缓存):基于namespace级别的缓存,一个namespace对应一个二级缓存 <mapper namespace="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper">
工作机制:
一个会话,查询一条数据,这个数据就会被放在当前会话的一级缓存中;
如果会话关闭,一级缓存中的数据会被保存到二级缓存中;新的会话查询信息,就可以参照二级缓存中的内容;(二级缓存只有在 SqlSession 关闭或提交之后才会生效)
不同namespace查出的数据会放在自己对应的缓存中(map)
使用:
(二级缓存默认不开启,需要手动配置 )在全局配置文件中 开启全局二级缓存配置:
<settings> <!--显式的指定每个我们需要更改的配置的值,即使他是默认的。防止版本更新带来的问题 --> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> </settings>去
mapper.xml中配置使用二级缓存:<cache></cache><mapper namespace="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper"> <cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" readOnly="false" size="1024"></cache>cache标签的属性:
eviction: 缓存的回收策略:- LRU (默认) – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
- FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
- SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
- WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
flushInterval:缓存刷新间隔缓存多长时间清空一次,默认不清空。单位是毫秒
readOnly: 是否只读:true:只读:mybatis认为所有从缓存中获取数据的操作都是只读操作,不会修改数据。
mybatis为了加快获取速度,直接就会将数据在缓存中的引用交给用户。不安全,速度快
false:非只读 (默认):mybatis觉得获取的数据可能会被修改。
mybatis会利用序列化&反序列的技术克隆一份新的数据给你。安全,速度慢
size:缓存存放多少元素;代表缓存最多可以存储多少个对象,太大容易导致内存溢出type:指定自定义缓存的全类名;(默认就是 namespace 的名称)
注意:POJO 需要实现序列化接口
public class Employee implements Serializable{ }
3. 缓存相关设置
和缓存有关的设置/属性:
cacheEnabled=true:开启二级缓存
false:关闭缓存(二级缓存关闭)(一级缓存仍然可用)
- 每个 select 标签都有
useCache="true"(默认)
配置这个select是否使用二级缓存。一级缓存一直是使用的
- 每个增删改标签默认
flushCache="true":sql执行以后,会同时清空一级和二级缓存。
查询标签默认 flushCache="false"
sqlSession.clearCache();清除当前session的一级缓存;当在某一个作用域 (一级缓存Session/二级缓存 namespace) 进行了增删改 操作后,默认该作用域下所有 select 中的缓存将被 clear。
4. Mybatis 的缓存原理

5. 第三方缓存 EhCache 整合
EhCache 是一个纯Java的进程内缓存框架,具有快速、精 干等特点,是Hibernate中默认的CacheProvider。
整合步骤如下:
① 导入 ehcache 包,以及Mybatis整合包,日志包
ehcache-core-2.6.8.jarmybatis-ehcache-1.0.3.jarslf4j-api-1.6.1.jarslf4j-log4j12-1.6.2.jar
② 编写ehcache.xml配置文件
该配置文件放在 conf 文件夹下,和 全局配置配置文件 为同级目录
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd">
<!-- 磁盘保存路径 -->
<diskStore path="D:\44\ehcache" />
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
</defaultCache>
</ehcache>
属性说明:
- diskStore:指定数据在磁盘中的存储位置。
- defaultCache:当借助
CacheManager.add("demoCache")创建Cache时,EhCache便会采用< defalutCache />指定的的管理策略
以下属性是必须的:
- maxElementsInMemory - 在内存中缓存的element的最大数目
- maxElementsOnDisk - 在磁盘上缓存的element的最大数目,若是0表示无穷大
- eternal - 设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断
- overflowToDisk - 设定当内存缓存溢出的时候是否将过期的element缓存到磁盘上
以下属性是可选的:
- timeToIdleSeconds - 当缓存在EhCache中的数据前后两次访问的时间超过timeToIdleSeconds的属性取值时,这些数据便会删除,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大
- timeToLiveSeconds - 缓存element的有效生命期,默认是0.,也就是element存活时间无穷大
- diskSpoolBufferSizeMB 这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小.默认是30MB.每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区.
- diskPersistent - 在VM重启的时候是否启用磁盘保存EhCache中的数据,默认是false。
- diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds - 磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒。每个120s,相应的线程会进行一次EhCache中数据的清理工作
- memoryStoreEvictionPolicy - 当内存缓存达到最大,有新的element加入的时候, 移除缓存中element的策略。默认是LRU(最近最少使用),可选的有LFU(最不常使用)和FIFO(先进先出)
③ mapper 中配置 cache标签
<mapper namespace="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper">
<cache type= "org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"></cache> 若想在命名空间中共享相同的缓存配置和实例。 可以使用 cache-ref 元素来引用另外一个缓存。
<mapper namespace="com.smallbeef.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper">
<cache-ref namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper"/>📚 References
-
课程配套百度网盘资源:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1bH-d1yBugAr0DjGzx7DGIA
提取码:nsct
🥝 公众号 江南一点雨 相关教程



